Bachelor's Thesis: Implementing DISTANA in PyTorch Geometric and Deep Graph Library
Thesis: “Implementing DISTANA in PyTorch Geometric and Deep Graph Library”
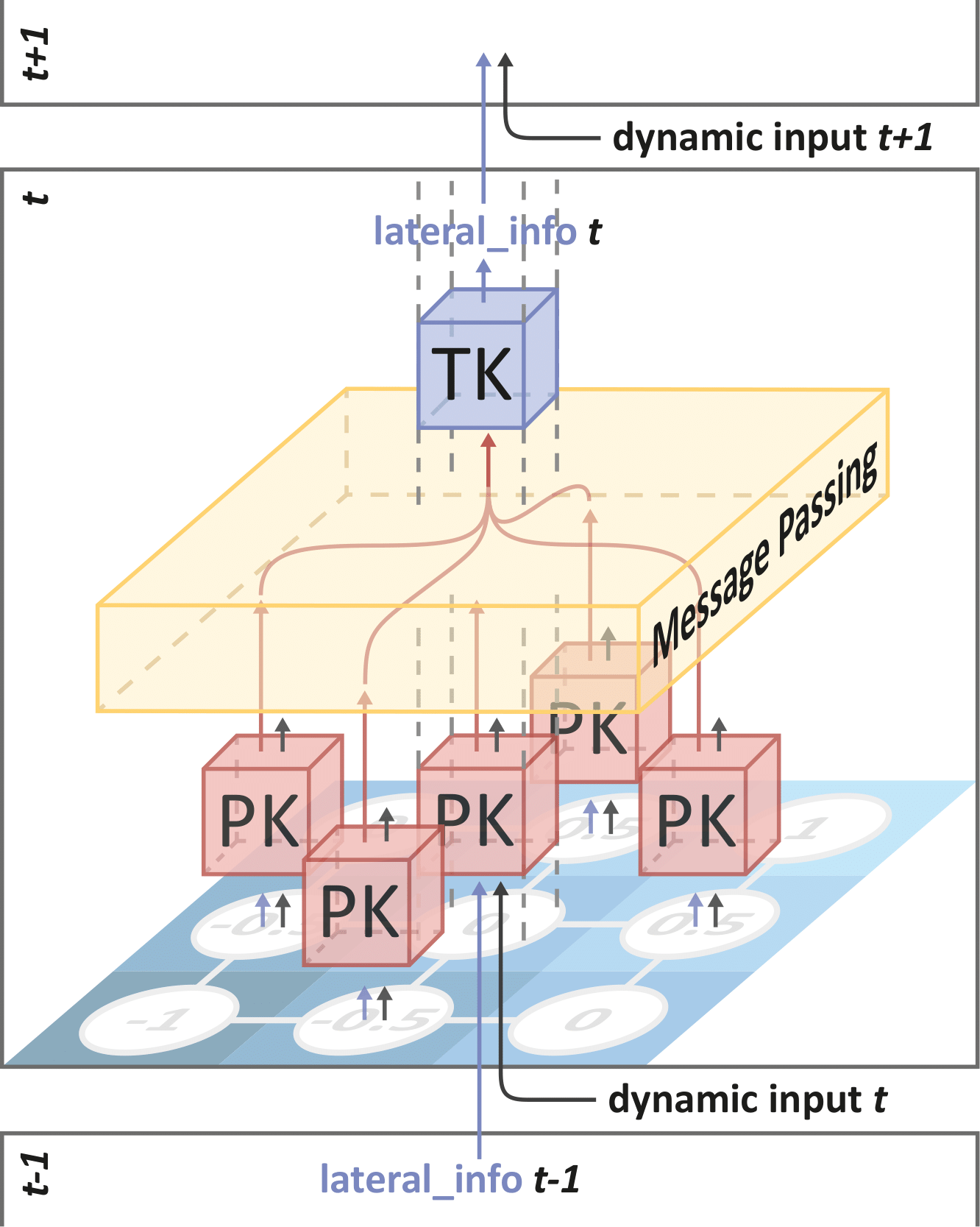
The goals of this work are twofold: (a) make DISTANA available on the increasingly popular APIs and to investigate PyTorch Geometric’s and Deep Graph Library’s usability when it comes to implementing a self-developed model, and (b) compare DISTANA to other GNN models in PyTorch Geometric and Deep Graph Library in terms of accuracy and computational complexity (i.e. processing speed) on different benchmarks.
While traditional neural networks have achieved remarkable results in many different domains, they are not suited to deal with non-euclidean data types such as graphs. To address this limitation, the development of Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) has caused great results in previously unsuccessful domains. One of these novel GNNs is DISTANA, an architecture that aims to learn the underlying causes of spatio-temporal processes. In previous work, DISTANA has already shown promise as an architecture for predicting such processes compared to other architectures. Therefore, in this thesis, DISTANA is implemented in the PyTorch Geometric (PyG) and Deep Graph Library (DGL) libraries, both of which offer environments for implementing custom GNN architectures. Results show that DISTANA performs much better than other state-of-the-art GNNs when predicting the spatio-temporal process of a two-dimensional wave propagation both in terms of generalization and accuracy. Reasons for this success are discussed, including DISTANA’s position awareness capability, which is unique compared to other GNNs.
This work continues into my work as a Research Assistant at the University of Tübingen, where I compare different traditional Neural Network architectures against Graph Neural Networks for the task of spatio-temporal forecasting in the context of Weather Data.